How can we help?
Search for answers or browse our knowledge base
Multiple transposition and Anonymisation of items
Transposition allows cross-tabulations to be simulated.
The cross-tabulated dimensions in the table must contain a limited number of terms and conditions that are fixed when the components are created in Design.
However, even if these terms are in a fixed number, the transposition makes it possible to reproduce an operation where the terms would be defined when the questionnaire is launched or when the data is entered.
NB: The fixed number of modalities for each of the dimensions of the transposition is an important point.
This is commonly used as a filter for the data, especially in the case of anonymisation of dates (even if many dates are placed in the data feeding the transposition, only the dates mentioned by the transposition will be used).
This is also a consideration since additional modalities (not specified when designing the qst) are simply ignored.
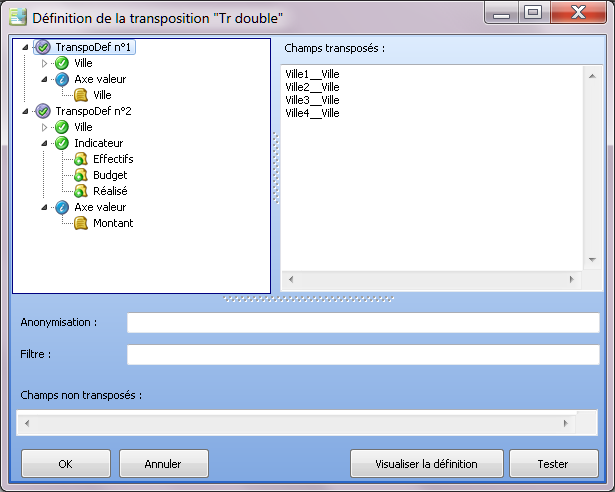
Double transposition
Starting with the following questionnaire asking for headcount, budget and output per country:
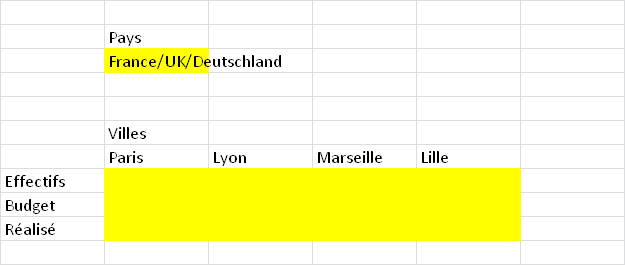
The cities in the columns are country-specific.
If we want to use the same questionnaire for different countries, we need to use city numbers within the country and not the names of the cities.
We will designate the cities within each country as City1, City2, … These anonymous cities will be used in the component headers:
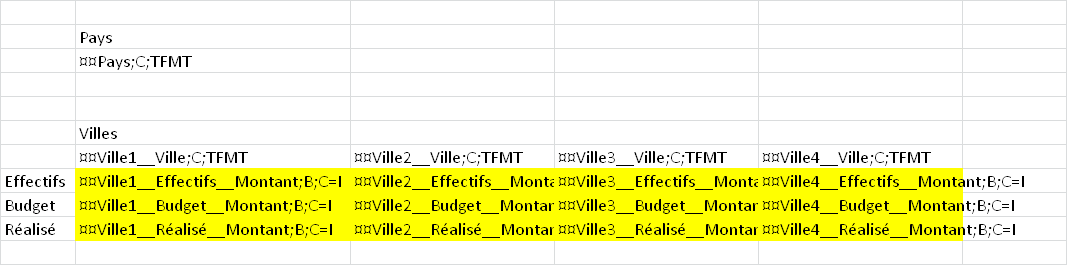
The transposition used will be as follows:
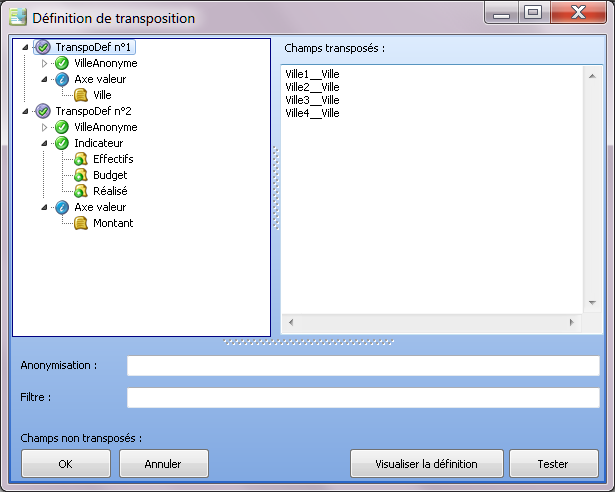
The components allowing to display the names of the cities could very well be input boxes or drop-down lists instead of controls: the correspondents could thus specify the cities for which they fill in the information.
The axis CityName must be present in the input data and contain the different values designated by the transposition: City1, City2
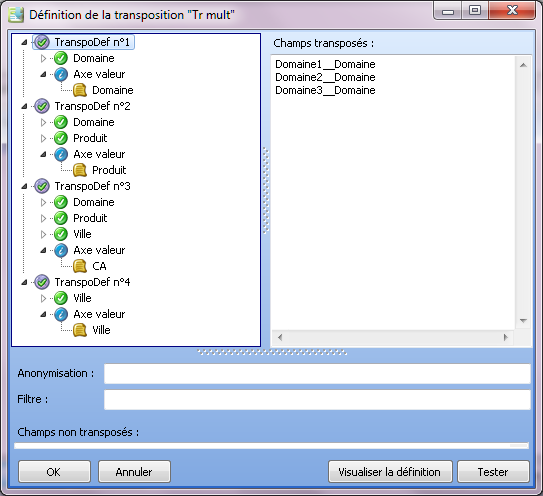
Multiple transposition
The following example is simply an extension of the double transposition.
The questionnaire asks for a list of products that have achieved more than 30% of sales in each domain.
The domains and products are country-specific. The first 2 areas are pre-filled when the questionnaire is sent.

Here are the component statements and the transposition implemented:
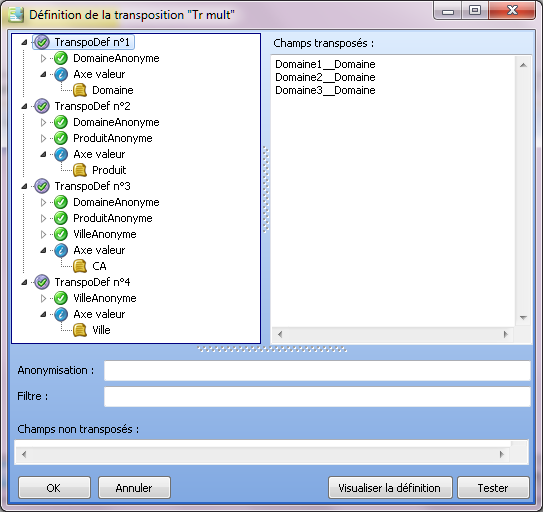
To construct the two transpositions AnonymousDomain;{Domain} and AnonymousCity;{City}, it is necessary to deselect City from the Value axis for the first two-dimensional transposition and then use the right click (under the transposition tree) to add a two-dimensional transposition branch for City (which is now no longer used by the first transposition).
Using a pattern for this questionnaire would probably be more complex than implementing it through a transposition (it would certainly require multiple patterns and using a transposition to override the uniqueness constraints on component headers).
Consistency of a multiple transposition
If multiple transposition allows to manage complex cases where the items of some dimensions are variable, it must respect a rule regarding the branches of the transposition definitions:
A branch must contain all the axes, excluding the values mentioned in the other branches.
The following transposition will be incorrect because the City and Country fields (non-value fields) are not contained in the same branch.
traxes1 City;{Direction}
traxes2 Country;{CA}
Anonymisation of items
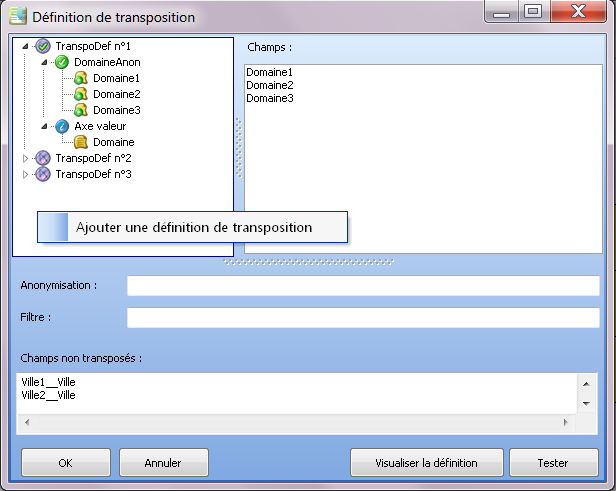
Multiple transposition often requires the presence of an anonymisation axis in the data at the time of the campaign launch ( AnonymousCity in the example of double transposition).
The anonymisation of items makes it possible to dispense with the construction of this or these anonymisation axes. This can greatly simplify the views used at launch.
Example of item anonymisation in the case of double transposition (the questionnaire is identical to the previous example):
Example of item anonymisation in the case of double multiple transposition (the questionnaire is identical to the previous example):
Some constraints on the use of item anonymisation:
- The anonymous items used in the component headers are constructed by taking the original field and adding a number (1, 2, …)
- The axis to be anonymised must be present as a Value axis and as a standard axis in the same branch of definition of the transposition
- The other axes present in the same definition branch express the context in which the item anonymisations are performed: Cities within each country or products within each country and each domain are numbered.
- The data should be sorted along the axes expressing the context
The context of anonymisation is important: if items are to be anonymised in rows and columns, the transposition definitions must be separated when an axis is anonymised to define the anonymisation context precisely.
The transposition context implicitly includes the diffusion axes.
If the anonymisation context for an axis includes axes belonging to the parent compartments (pattern or multi-tab), a duplicate of these axes should be included in the transposition to express the anonymisation context.
Finally, item anonymisation can be used in a transposition where date anonymisation already exists (if the anonymised date field is different from the field containing the anonymised items).



